If you’re involved in programming or any aspect of IT, you might find yourself wanting to install Ubuntu on your machine. However, it’s important to note that some users experience an issue where they cannot boot into Windows after setting up Ubuntu as a dual-boot operating system. In this article, we’ll explore this problem and provide solutions to help you resolve it.
Solutions for Resolving Windows Boot Issues After Installing Ubuntu
If Windows 11/10 won’t start following your Ubuntu installation, consider trying the solutions outlined below.
- Rebuild the BCD File and MBR
- Use Startup Repair
- Adjust Boot Order
- Update the GRUB Bootloader
- Set the Windows Partition as Active
Let’s dive deeper into each of these solutions.
1] Rebuild the BCD File and MBR
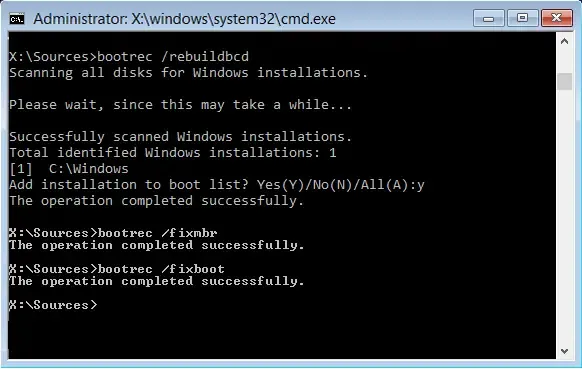
The Boot Configuration Data (BCD) file is essential as it contains the configuration information that the Windows Boot Manager relies on to manage the boot process. The Master Boot Record (MBR) is also crucial, located at the start of partitioned drives. If either of these files becomes corrupted, booting issues may arise. To resolve these issues, you’ll need to rebuild them. Follow these steps:
- First, create a bootable Windows installation media using another computer, and boot your affected device with it.
- Once on the Windows Startup screen, select Repair your computer.
- Go to Troubleshoot > Advanced Options > Command Prompt.
- When the Command Prompt opens, enter the following commands, one at a time:
bootrec /fixmbr
bootrec /fixboot
bootrec /rebuildbcd
After completing these commands, restart your computer and verify if the problem remains.
2] Use Startup Repair
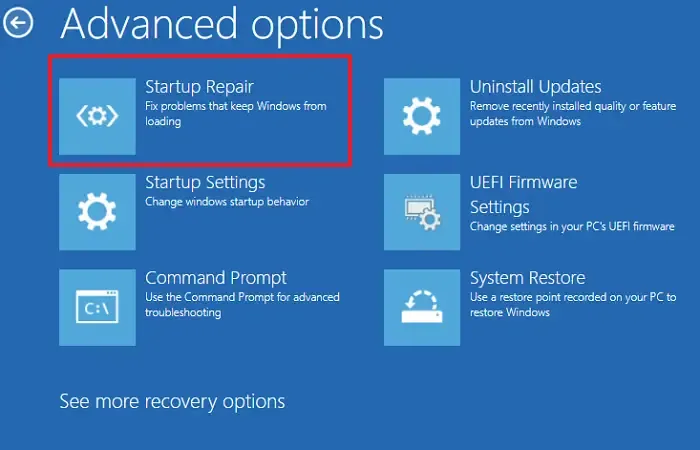
If your machine is facing issues like missing or corrupt system files, damaged boot configuration data, problematic drivers, or registry errors, running Startup Repair can help diagnose and fix these problems. To utilize this tool, follow these steps:
- Create installation media and boot it on the troubled computer.
- Once booted, select Repair your computer.
- Navigate to Troubleshoot > Advanced Options.
- Click on Startup Repair.
Follow the on-screen prompts to finish the repair process. Once complete, check if the issue is resolved.
3] Adjust Boot Order
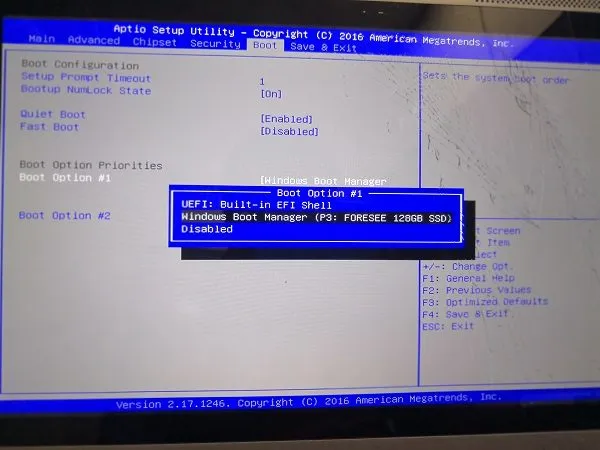
If Windows and Ubuntu are installed on separate drives, ensure that the boot order is set to prioritize the disk with Windows. This can often be overlooked during the Ubuntu installation process. To adjust the boot order, follow these instructions:
- Begin by entering your UEFI or BIOS settings.
- Set the boot order so that the hard disk containing Windows is the first option. Typically, GRUB (the bootloader for Ubuntu) is favored since it recognizes both operating systems.
- Save the changes and exit the BIOS.
After adjusting the boot order, proceed to the next step.
4] Update the GRUB Bootloader
Once the boot order is set appropriately, the next step is updating the GRUB Bootloader for dual-boot functionality. The GRUB bootloader is responsible for managing the boot process for Linux-based operating systems and allows users to select their preferred OS during startup. To update it, follow these steps:
sudo update-grub
After executing the command, restart your system to see the option to select between Windows or Ubuntu at boot.
5] Set the Windows Partition as Active
If both operating systems are installed on one disk, the Windows partition may have been inadvertently set as inactive. Here’s how to reactivate it:
- Boot your computer using the installation media.
- Navigate to Repair your computer > Troubleshoot > Advanced Options > Command Prompt.
- Start the diskpart utility by typing
diskpartand pressing Enter. - Select the disk by entering:
select disk 0. - Type
list partitionto display all partitions, then select the one where Windows is installed using:select partition <partition-number>. - Type
activeto mark it active and press Enter.
Finally, reboot the computer.
Why Won’t My Computer Boot After Installing Ubuntu?
Several factors may contribute to your computer’s inability to boot post-Ubuntu installation, including an outdated GRUB partition. It is crucial to update the GRUB after adding Ubuntu to a machine that already runs another OS. Also, ensure the boot order is set up correctly.
How Can I Access Windows After Installing Ubuntu?
If you wish to switch between Windows and Ubuntu, setting up a dual boot is essential when installing multiple operating systems on a single device. This setup allows you to choose your desired OS every time you start the computer.


